Training Blocks - Macro, Meso and Micro cycles - Simply Put: How to Structure Your Training for Success
Training Blocks Explained: How to Structure and Apply Them for Maximum Results
What are they
How to apply them
How long should they be
Strength - Endurance - Hyrox
Conditioning - General Preparation, Pre-Comp and Comp
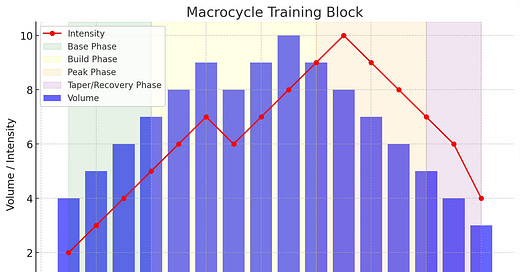
What is a training block?
A training block can be described as a structured period of training with a specific focus. Eg: strength, endurance, running, etc
If we break this down further we can look at the specific cycles within these training blocks.
Macrocycle: A macrocycle is usually about 12 months broken down into smaller time frames with specific targets. eg: Hyrox Race
Mesocycle: 4-6 weeks block of training with a specific structure and purpose:
eg: endurance (running)
Microcycle: Typically 1 week and sits within the Mesocycle.
Let’s look a simple example of how they fit together.
The macrocycle is our 12-month plan to complete a Hyrox race. Within this 12-month plan, we have several things we need to focus on. Strength, Endurance, Compromised Running, Erg Skills, Speed, etc.
General Preparation.
1. General Preparation Phase: This is indeed a foundational phase in many training programs. It's designed to build a base level of fitness before moving on to more specific or intense training.
2. Duration: 4-6 week timeframe is a typical length for this phase, though it can vary depending on the individual's goals and overall training plan.
3. Purpose: The main goal of this phase is to condition the body to handle higher loads in future training phases.
4. Activities: For the new Hyrox Competitor activities like (cycling, walking/running, and general strength training) will all form part of this phase. These exercises help develop overall cardiovascular fitness and basic strength.
5. Focus on general conditioning: The emphasis is on building a broad base of fitness rather than sport-specific skills of high-intensity work. Spend time on your feet walking and running and time in there gym doing functional movements that use multiple muscles groups or compound moments like the squats, leg press, lunges, etc.
This approach allows the body to adapt gradually to increased physical demands, reducing the risk of injury when more intense, specific training begins.
How to structure a typical week in general preparation phase:
This is a very simplified overview for a beginner athlete.
Monday:
30-45 minutes of low-intensity cardio (e.g., jogging or cycling)
20-30mins Full-body strength training (2-3 sets of 12-15 reps)
Tuesday:
45-60 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio (e.g., swimming, rowing, cycling)
Wednesday:
Active recovery day: 30 minutes of walking or yoga
Thursday:
45 mins Full body strength training. 2-3 sets 8-12 reps
Friday:
45-60 minutes of steady-state cardio (cycling, incline walking on treadmill, stair climber)
Saturday:
🏃♂️🚴 🥾Longer duration (60-90 minutes) low-intensity activity (e.g., hiking or cycling)
Sunday:
Rest day or very light activity (walking or yoga)
💪 Stay consistent ♾️
Rod